[ relational data model ]
* set
- 서로 다른 elements를 가지는 collection. (중복x)
- 하나의 set에서 elements의 순서는 중요하지 않음.
e.g.) {1, 2, 11, 4, 7}
* relation in mathematics

Cartesian product A X B = { (a, b) | a ∈ A and b ∈ B } _ 가능한 모든 pair의 조합

binary relation ⊆ A X B _ Cartesian product 의 부분집합(세 개의 pair)
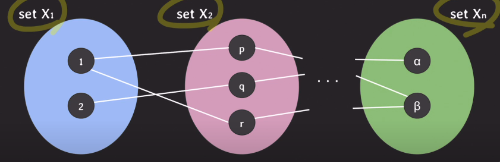
n-ary relation ⊆ X1 x X2 x ... x Xn
각각의 연결된 리스트 => 튜플(n-tuple)
< 수학에서의 relation >
- subset of Cartesian product ( Cartesian product 의 부분집합)
- set of tuples (튜플들의 집합)
* relational data model
set => 도메인 (값들의 집합)
* student relation 예시 *
domain 정의
- students_ids : 학번 집합, 7자리 integer 정수
- human_names : 사람 이름 집합, 문자열
- university_grades : 대학교 학년 집합, {1, 2, 3, 4}
- major_names : 대학교에서 배우는 전공 이름 집합
- phone_numbers : 핸드폰 번호 집합
- phone_numbers : 핸드폰 번호 집합 (비상연락망)
=> 동일한 도메인에 대해서 사용목적(역할)이 다른 경우 => attribute로 표현.
- students_ids : id
- human_names : name
- university_grades : grade
- major_names : major
- phone_numbers : phone_num
- phone_numbers : emer_phone_num
각각의 튜플들을 효과적으로 표현하기 위해 relational table 사용

* domain : set of atomic values
* domain name : 도메인 이름
* attribute (속성, ) : domain이 relation에서 맡은 역할 이름
* tuple (행) : 각 attribute의 값으로 이루어진 리스트, 일부 값은 NULL일 수 있다.
* relation : set of tuples
* relation name : relation의 이름
* relation schema
- relation의 구조를 나타냄.
- relation 이름과 attributes 리스트로 표기.
e.g.) STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num)
- attributes와 관련된 constraints도 포함.
* degree of a relation
- relation schema에서 attributes의 수
e.g.) STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num) => degree 6
* relation (or relation state)
- set of tuples 튜플들의 집합. (임의의 시점에서의 튜플들의 집합_실제 데이터)
* relational database
- relational data model에 기반하여 구조화된 database.
- relational database는 여러 개의 relations로 구성된다.
* relational database schema
relation schemas set + integrity constraints set
[ relation의 특징 ]
- relation은 중복된 tuple을 가질 수 없다. (relarion is set of tuples)

- relation의 tuple을 식별하기 위해 attribute의 부분 집합을 key로 설정한다.

- relation에서 tuple의 순서는 중요하지 않다. (정렬기준이 다양)
- 하나의 relation에서 attribute의 이름은 중복되면 안된다.
- 하나의 tuple에서 attribute의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
- attribute는 atomic 해야 한다. (composite or multivalued attribute 허용 안됨)

=> address인 '서울특별시 강남구 청담동'이 atomic 하지 않음 (composite attribute)
'서울특별시' / '강남구' / '청담동' 으로 쪼갤 수 있음.
=> major는 '컴공, 디자인' 은 두개의 값을 가지고 있음 (multivalued attribute)
'컴공' / '디자인' 으로 쪼갤 수 있음.
* Null의 의미
- 값이 존재하지 않는다.
- 값이 존재하나 아직 그 값이 무엇인지 알지 못한다.
- 해당 사항과 관련이 없다.

=> 졸업하기 위해 토익점수 제출이 필요한 상황이라면,
- 시험을 안봐서 토익점수가 없는 경우
- 시험을 봤지만 제출하지 않은 경우
- 제출했지만 누락되었거나, 정보가 업데이트 되지 않은 경우
등등 다양한 의미로 해석가능.
* super key (슈퍼키)
- relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별할 수 있는 attribute set.
e.g.) PLAYER (id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)
super key => {id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date} , {id, name}, {name, team_id, back_number}, .... etc
* candidate key (후보키)
- 어느 한 attribute라도 제거하면 unique하게 tuples를 식별할 수 없는 super key.
- key or minimal superkey
e.g.) PLAYER (id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)
candidate key => {id}, {team_id, back_number}
* primary key (기본키)
- relation에서 tuple를 unique하게 식별하기 위해 선택된 candidate key.
e.g.) PLAYER (id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)
primary key => {id}, {team_id, back_number}
보통 attribute 수가 적은 것으로 선택
* unique key
- primary key가 아닌 candidate keys
- alternate key
e.g.) PLAYER (id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)
unique key =>{team_id, back_number}
* foreign key (외래키)
- 다른 relation의 PK를 참조하는 attributes set.
e.g.) PLAYER (id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date) 와 TEAM (id, name, manager)가 있을 때
foreign key => PLAYER의 {team_id}
* constraints 뜻
- relational database의 relations들이 언제나 항상 지켜줘야 하는 제약 사항.
* implicit constraints
- relational data model 자체가 가지는 constraints.
- relation은 중복되는 tuple을 가질 수 없다.
- relation 내에서는 같은 이름의 attribute를 가질 수 없다.
* schema-based constraints
- 주로 DDL을 통해 schema에 직접 명시할 수 있는 constraints.
- explicit constraints.
1) domain constraints
- attribute의 value는 해당 attribute의 domain에 속한 value여야 한다.

=> grade는 1, 2, 3, 4 학년 중 하나여야 한다.
2) key constraints
- 서로 다른 tuples는 같은 value의 key를 가질 수 없다.
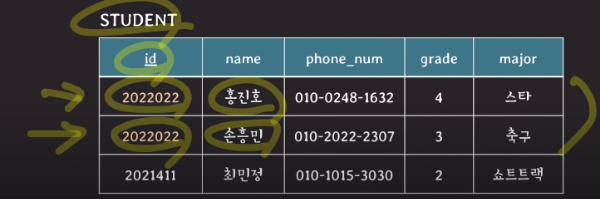
3) NULL value constraint
- attribute가 NOT NULL로 명시됐다면 NULL을 값으로 가질 수 없다.

4) entity integrity constraint
- primary key는 value에 NULL을 가질 수 없다.

4) referential integrity constraint
- FK와 PK와 도메인이 같아야 하고, PK에 없는 values를 FK가 값으로 가질 수 없다.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gjcbqZjlXjM&list=PLcXyemr8ZeoREWGhhZi5FZs6cvymjIBVe&index=2
'Database > MySQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터베이스(강의)] 6. SQL로 데이터 조회 (subquery / IN, EXIST, ANY, ALL) (0) | 2024.02.02 |
|---|---|
| [데이터베이스(강의)] 5. SQL로 데이터 조회 (Select) (0) | 2024.02.01 |
| [데이터베이스(강의)] 4. SQL (Insert / Update / Delete) (0) | 2024.01.30 |
| [데이터베이스(강의)] 3. SQL 기본 개념 및 SQL로 데이터베이스 정의 (0) | 2024.01.25 |
| [데이터베이스(강의)] 1. 데이터베이스 기본 개념 (0) | 2024.01.23 |



